Strength Training for Metabolism

Your metabolism isn't fixed—it can be improved. Muscle tissue burns more calories than fat tissue, even at rest. Building muscle through strength training increases your basal metabolic rate, meaning you burn more calories around the clock. This program is designed to maximize metabolic impact through strategic muscle building.
How Strength Training Boosts Metabolism
Muscle is metabolically active tissue. Each pound of muscle burns approximately 6-10 calories per day at rest, while fat burns only 2-3. Building even 5-10 pounds of muscle noticeably increases your daily calorie burn.
Strength training creates an "afterburn" effect called EPOC (excess post-exercise oxygen consumption). Your body continues burning elevated calories for 24-48 hours after a workout as it repairs muscle tissue.
Compound movements that work large muscle groups have the biggest metabolic impact. Squats, deadlifts, and rows burn more calories than isolation exercises because they involve more total muscle mass.
Metabolic Benefits of Strength Training
Higher Resting Metabolism
More muscle means more calories burned around the clock.
Post-Workout Burn
Elevated calorie burn for 24-48 hours after training.
Improved Insulin Sensitivity
Better nutrient partitioning—more to muscle, less to fat.
Better Body Composition
Replace fat with muscle for a leaner physique.
Sustainable Results
Muscle maintains metabolism during calorie restriction.
Age-Related Protection
Counteract the metabolic slowdown that comes with aging.
Program Overview
Who it's for: Anyone wanting to boost metabolism through muscle building
Don't have all this equipment? GymFriend can build you a custom program using whatever you have available.
Why These Exercises?
Each exercise in this program was selected for a specific reason. Here's why:
Dumbbell Goblet Squat
Large muscle groups = large metabolic impact.
Barbell Romanian Deadlift
Posterior chain development for significant muscle mass.
Dumbbell Bench Press
Upper body pressing for chest, shoulder, and tricep growth.
Cable One Arm Bent Over Row
Back muscle development—a large muscle group.
Dumbbell Lunge
Single-leg work for additional leg muscle development.
Dumbbell Seated Shoulder Press
Shoulder development contributing to total muscle mass.
The Complete 3-4 days Program
Follow this program consistently for best results. Start with weights that feel manageable and aim to increase gradually each week as you get stronger.
Want this program adjusted for your fitness level, goals, or schedule? GymFriend can create a personalized version just for you.
Building a Faster Metabolism
- Prioritize compound exercises that work multiple large muscle groups.
- Progressive overload is essential—continue challenging your muscles.
- Adequate protein intake (0.7-1g per pound bodyweight) supports muscle building.
- Don't slash calories too aggressively—you need fuel to build muscle.
- Sleep is crucial for muscle growth and metabolic function.
- Be patient—metabolic changes from muscle building take months, not weeks.
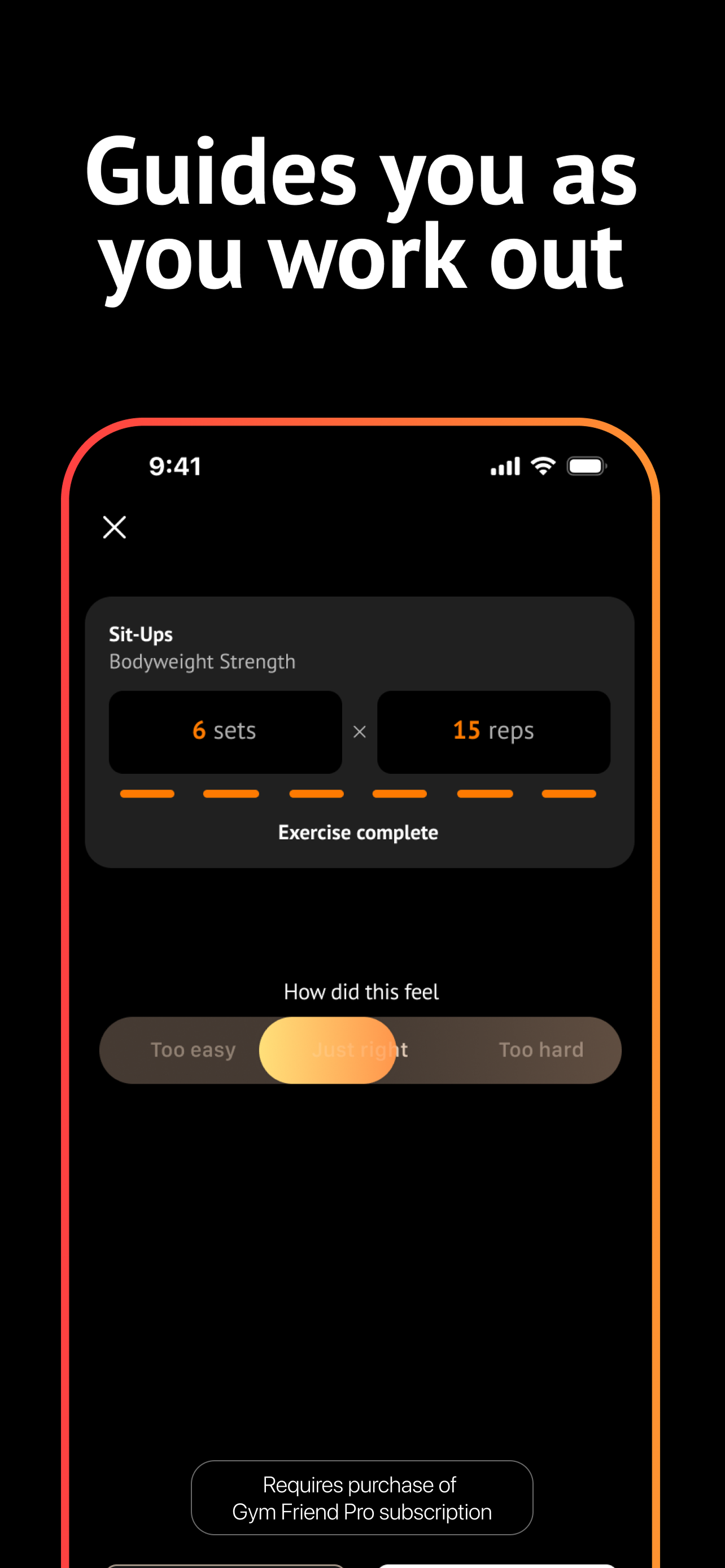
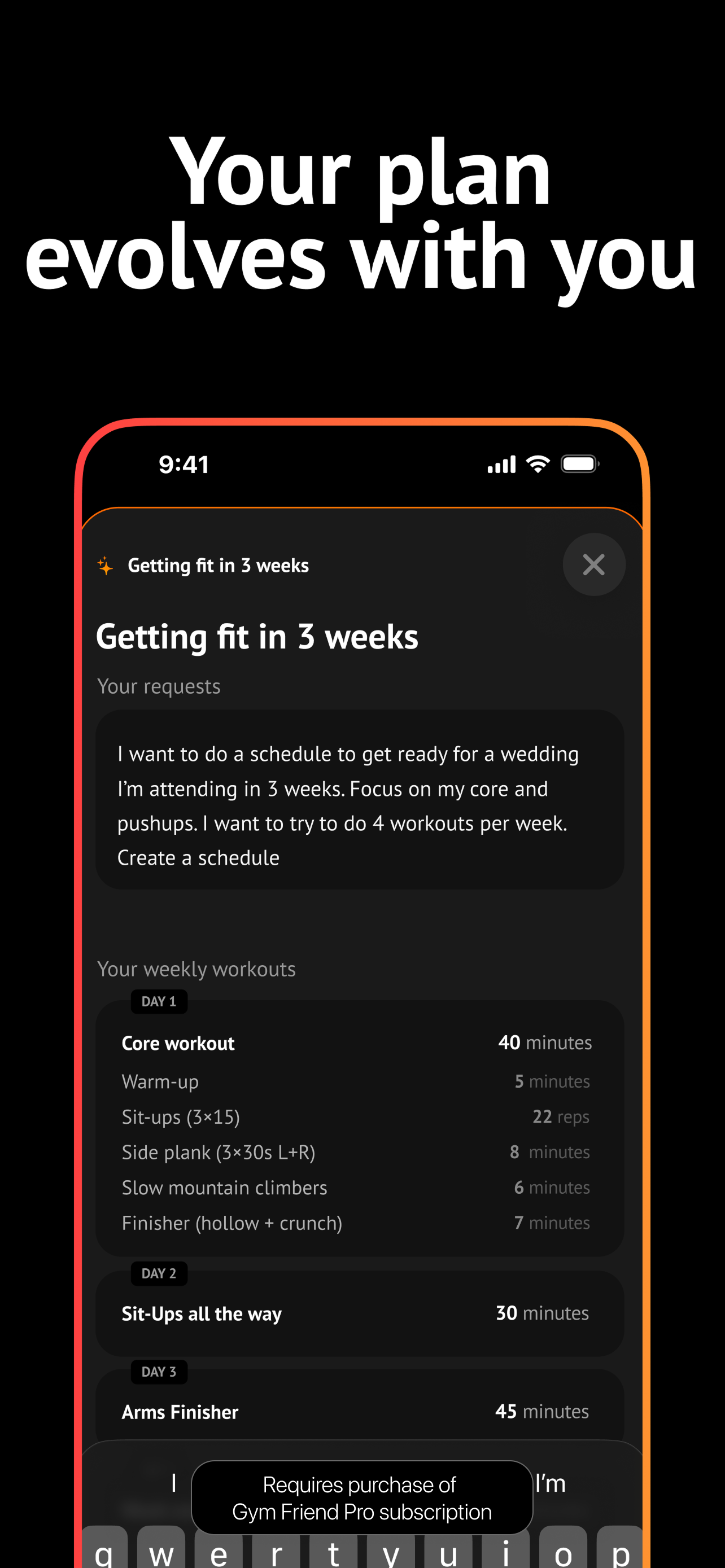
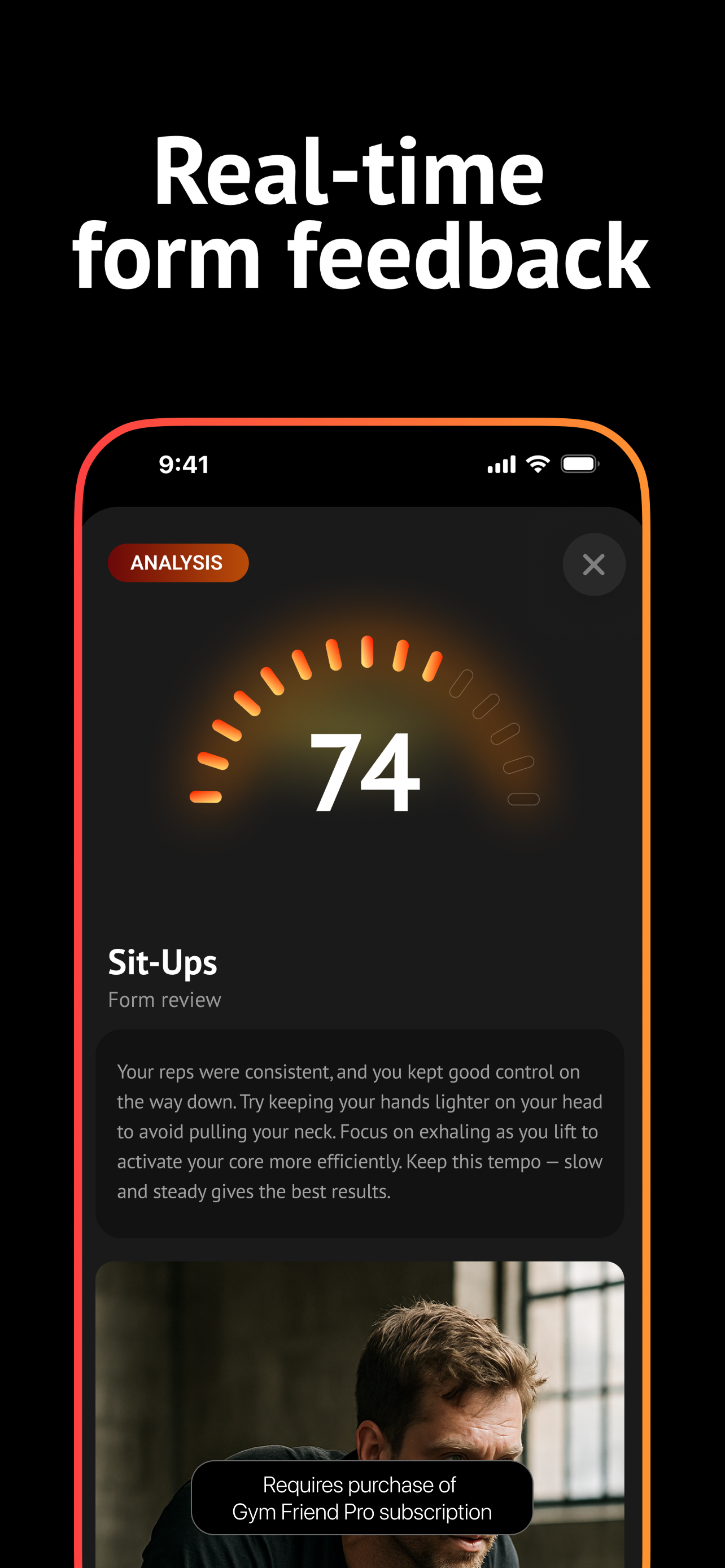
Edit your plan, track progress, and get realtime coaching
Frequently Asked Questions
How much can I increase my metabolism?
Each pound of muscle adds about 6-10 calories to your daily burn. Building 10 pounds of muscle could increase resting metabolism by 60-100 calories daily.
How long until I see metabolic changes?
EPOC effects happen immediately after workouts. Lasting metabolic increases from muscle building take 2-4 months of consistent training.
Should I do cardio too?
Cardio burns calories but doesn't build muscle. Include some for heart health, but prioritize strength training for metabolic improvement.
Can I build muscle while losing fat?
Yes, especially if you're new to training or returning after a break. Eat adequate protein and train consistently.
Does metabolism slow with age?
Yes, primarily due to muscle loss. Strength training counteracts this by maintaining or building muscle as you age.